Supreme Deferred Tax Liability Calculation Example

Bad debt expense recognized in income statement 25000.
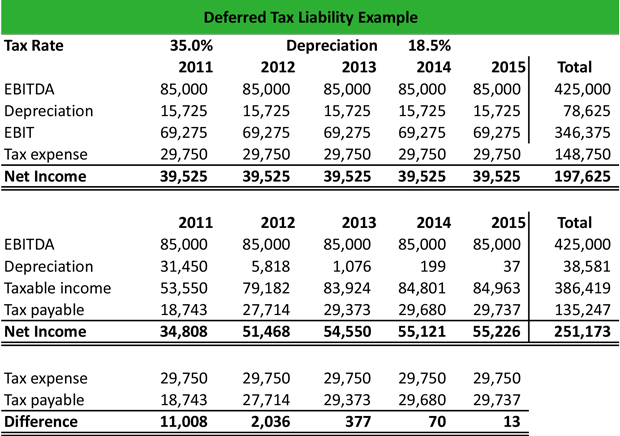
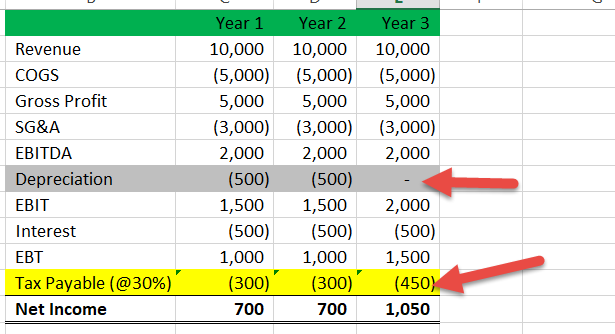
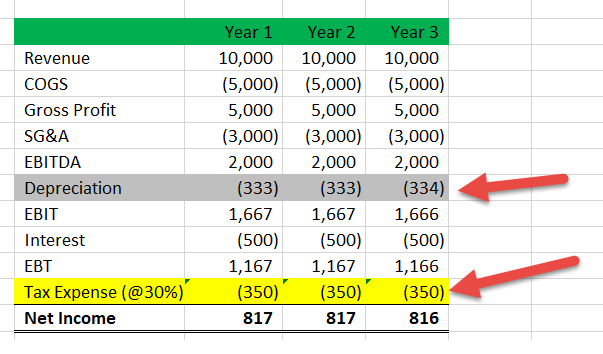
Deferred tax liability calculation example. Its useful life is determined to be 5 years therefore the depreciation charge amounts to 200 per year. The company records 240 800 30 as a deferred tax. Illustration of the purpose of deferred tax liabilities In 20X1 Entity A purchases a fixed asset that costs 1000.
Deferred Tax Calculation Example To see the effect of temporary timing differences on the calculation of the deferred tax liability consider the following example. Cover some of the more complex areas of preparation of a deferred tax computation for example the calculation of deferred tax balances arising from business combinations. Suppose taxable income is.
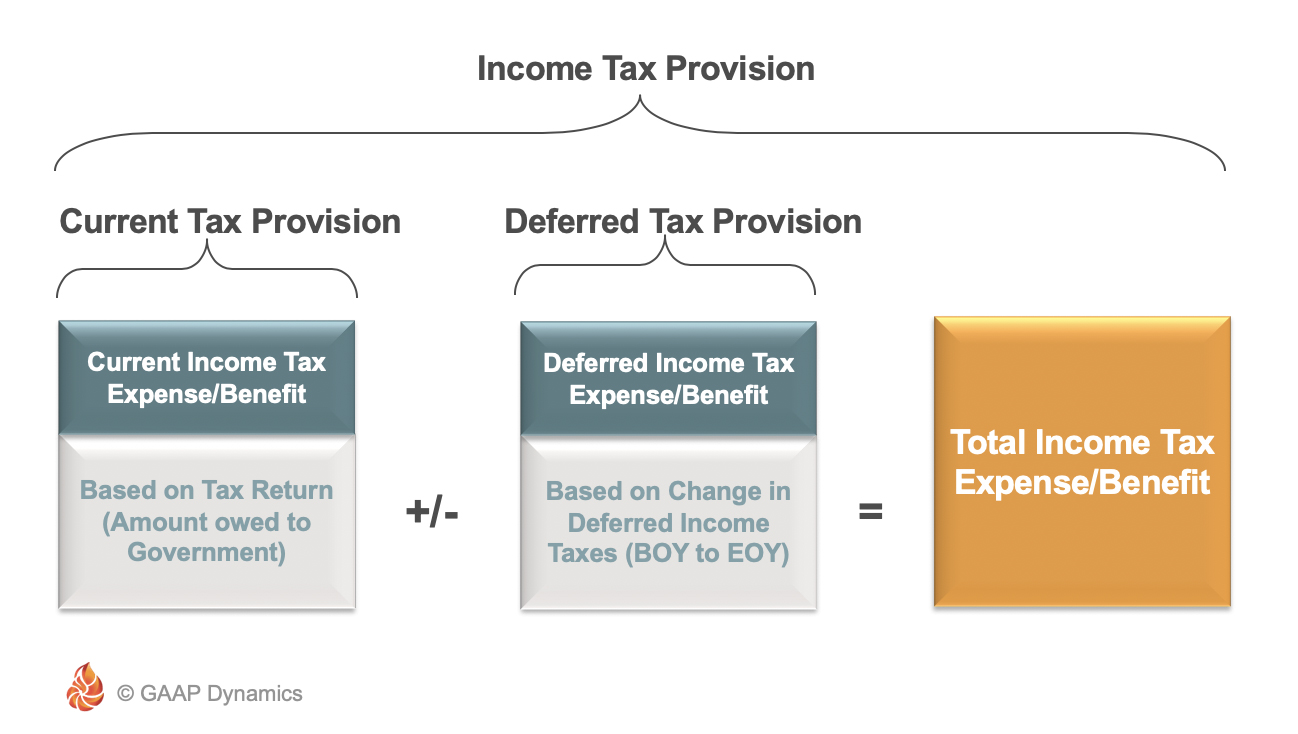
Thus the Company will record deferred tax assets DTA in the balance sheet. CU 15 900 calculation 2 above The deferred tax liability as of 31 December 20X4. Calculating a deferred tax balance the basics IAS 12 requires a mechanistic approach to the calculation of deferred tax.
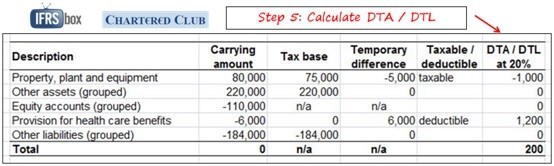
Tax base 400000. Carrying value is 0. The sections of the guide are as follows.
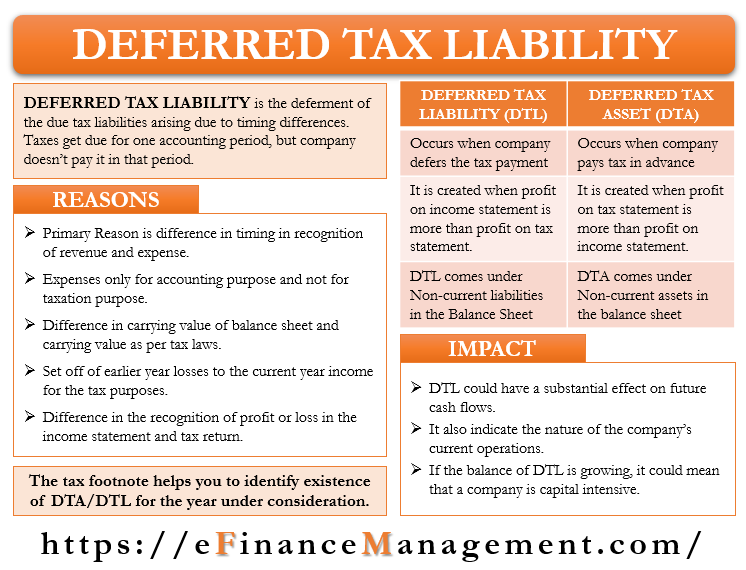
One other example of deferred tax liability is in how revenue is recognized. A firm has an asset with carrying value 500000. Example Calculation and impact of deferred tax liability and asset In the first year we have deferred our tax liability of Rs 3708 by charging higher depreciation in IT act compare to companies act.
For example if a company has an asset worth 10000 with a. These avenues create a disparity between the two financial reports thus generating a deferred tax liability. For example income profit before tax of ABC Ltd.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)


/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)