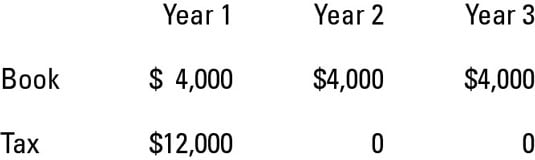Best Permanent Differences Tax Examples

Some examples of permanent differences are.
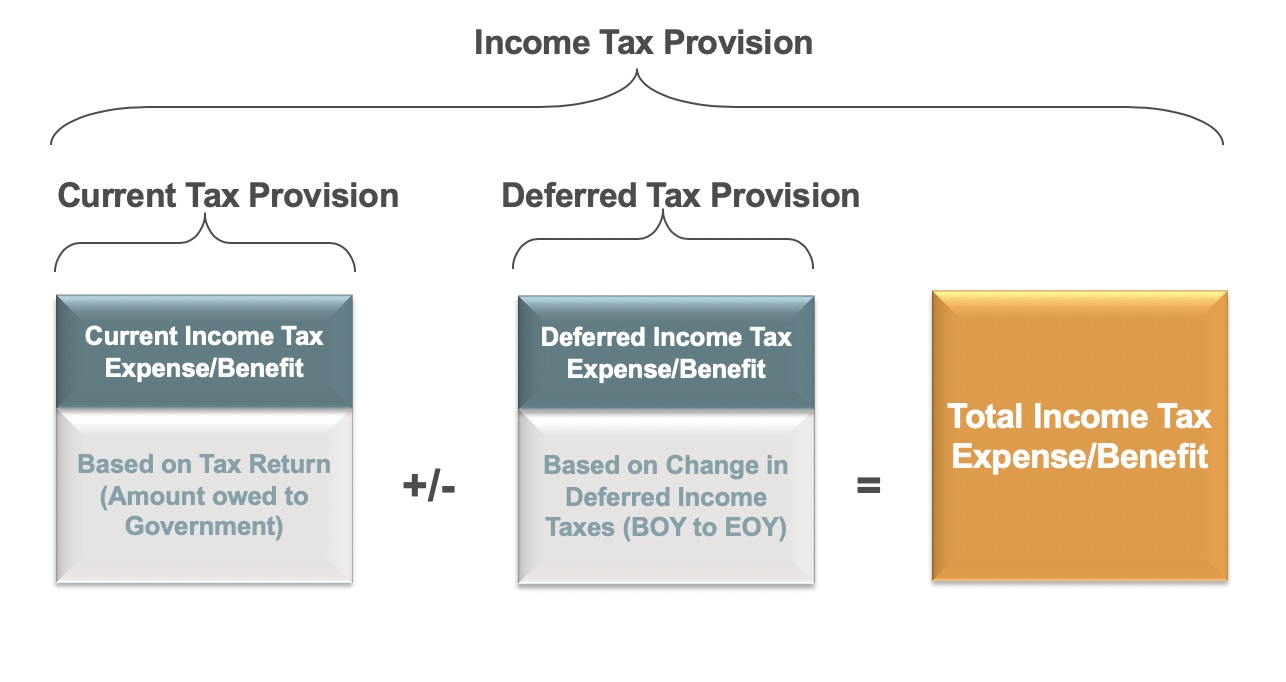
Permanent differences tax examples. Example of temporary difference for deferred revenue For example in 2019 ABC Internet Co. A permanent difference is a business transaction that is reported differently for financial and tax reporting purposes and for which the difference will never be eliminated. These do no adjust in future.
Some examples of non-taxable income include. Tax burden ETR 35 because in this example there are no temporary or other permanent differences. The following transaction types represent permanent differences.
Income or expense items that are not allowed by tax legislation and Tax credits for some expenditures directly reduce taxes. Examples of the items which give rise to permanent differences include. The permanent difference between pretax revenue and taxable income includes the difference caused by the event or transaction that can never be eliminated or reversed over the period.
Permanent differences have no effect on the taxes or other aspects of a business and are easy to deal with from an accounting perspective. Permanent differences are caused by statutory requirements. As with temporary differences quite a few accounting events lead to a permanent difference.
The non-taxable income is the income that exempts from tax and non-deductible expense is the expense that cannot deduct from taxable income. Received 10000 from its clients in advance for two years of internet service in 2020 and 2021. We do not make DTA DTL.
Chapter 19 Examples of Permanent Differences and Temporary Differences PERMANENT DIFFERENCES 1. Permanent differences result from non-taxable incomes and non-deductible expenses. In other words it is the difference between financial accounting and tax accounting that is never eliminated.