Smart Deferred Tax Computation Example

P buys debt instrument.
Deferred tax computation example. This example illustrates the consequences of recognising undiscounted amounts of deferred tax assets and the benefit of thinking in present value terms. For example income profit before tax of ABC Ltd. LesseeT Lessor L 5-year lease.
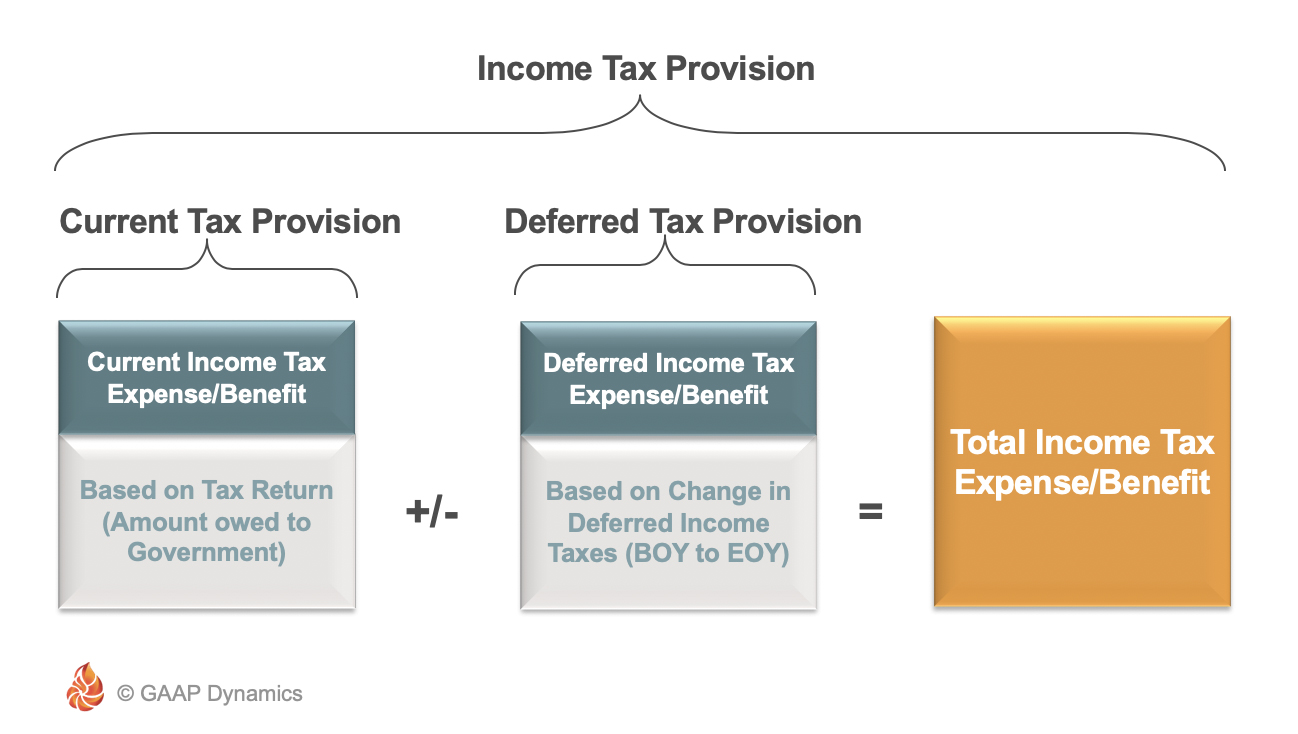
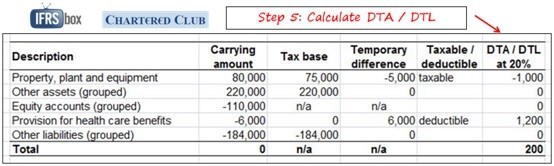
A deferred tax liability for temporary differences that will increase taxable profit taxable temporary differences. Cover some of the more complex areas of preparation of a deferred tax computation for example the calculation of deferred tax balances arising from business combinations. Deferred tax simple example.
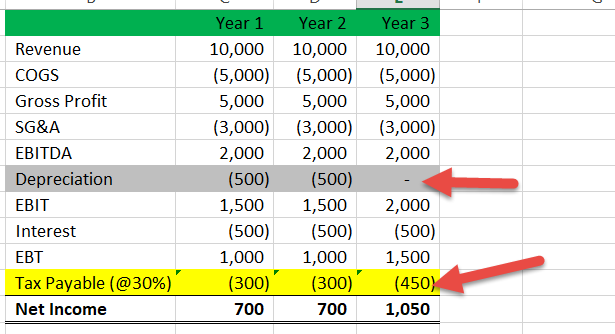
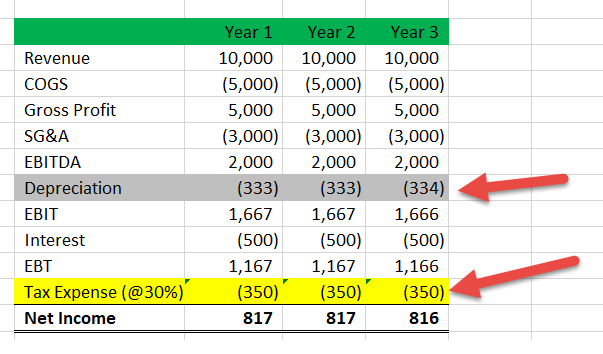
Deferred Tax Calculation As a simple example suppose a business has bought a long term asset for 3000 and decides it has a useful life of 3 years. Deferred Tax Calculation Example To see the effect of temporary timing differences on the calculation of the deferred tax liability consider the following example. And the lease liability under IFRS 16 are CU 435.
P expects to collect full 1000 ie. They purchased 2000 worth of equipment with the depreciation policy being 15 SL. Recognising deferred tax on leases.
The deferred tax represents the negative or positive amounts of tax owed by the Company. Concept of Deferred Tax. Its useful life is determined to be 5 years therefore the depreciation charge amounts to 200 per year.
So at the year end the balance is 1700. The depreciation expense each year will be 3000 3 1000. A deferred tax asset for temporary differences that will reduce taxable profit deductible temporary differences.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)

/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)





/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)