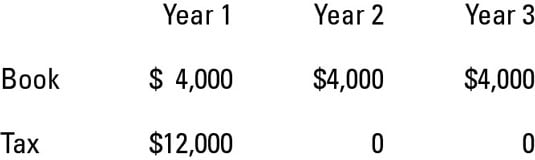Impressive Temporary Tax Differences Examples

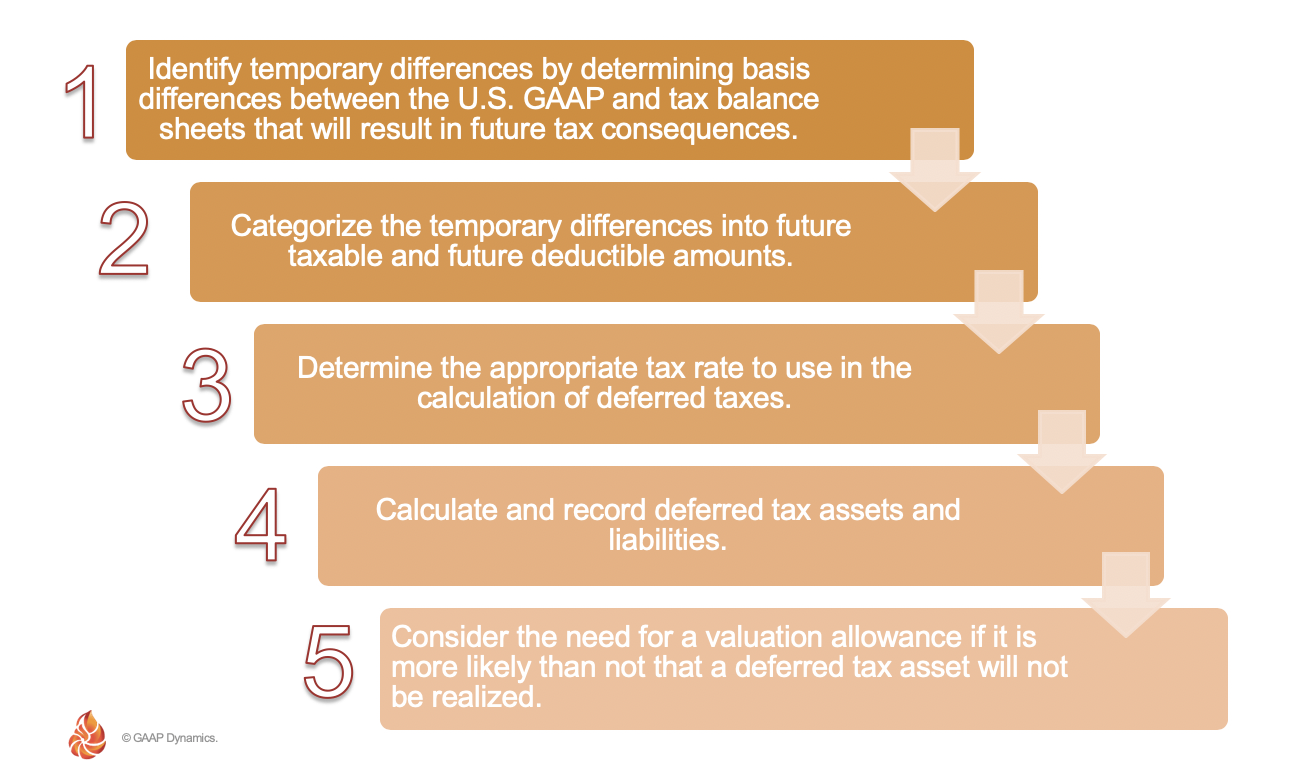
Taxable Temporary Differences The difference which results in taxable amounts in determining taxable profitloss of future periods.
Temporary tax differences examples. They lead to deferred tax liabilities. Example of Temporary Difference In 2017 XY Internet Co. Tax is charged at a rate of 25.
Fines and Penalties Meals and Entertainment Political Contributions Officers Life Insurance and Tax-exempt Interest. Examples of situations when taxable temporary differences arise and deferred tax liability is recognised are as follows. Received 20000 from its clients in advance for 2 years internet service in 2018 and 2019.
Example A company owns a 50000 municipal bond with a 4 coupon and has an effective tax rate of 50 and a statutory tax rate of 40. At the year-end there are taxable temporary differences of 10000. What is a temporary difference in tax expense.
Example 2 published accounts question. The following examples will help to illustrate when temporary differences arise versus permanent differences. For example in 2019 ABC Internet Co.
Tax differences arise because book income income c. For tax purposes non-deductible expenses are irrelevant as if they werent incurred. Taxable temporary differences are timing differences which cause taxable income in current period to be lower than pretax accounting income subject to taxes and hence income tax payable in current period to be lower than the accrual income tax expense.
In Example 2 another company has one book - tax difference that is permanent. Under Statement 96 all differences between the financial statement carrying amount and tax basis of inventories are temporary differences. To put this another way transactions that create temporary differences are recognized by both financial accounting and accounting for tax purposes but are recognized at different times.